A stain for lymphocyte subpopulations.
Intended Use :
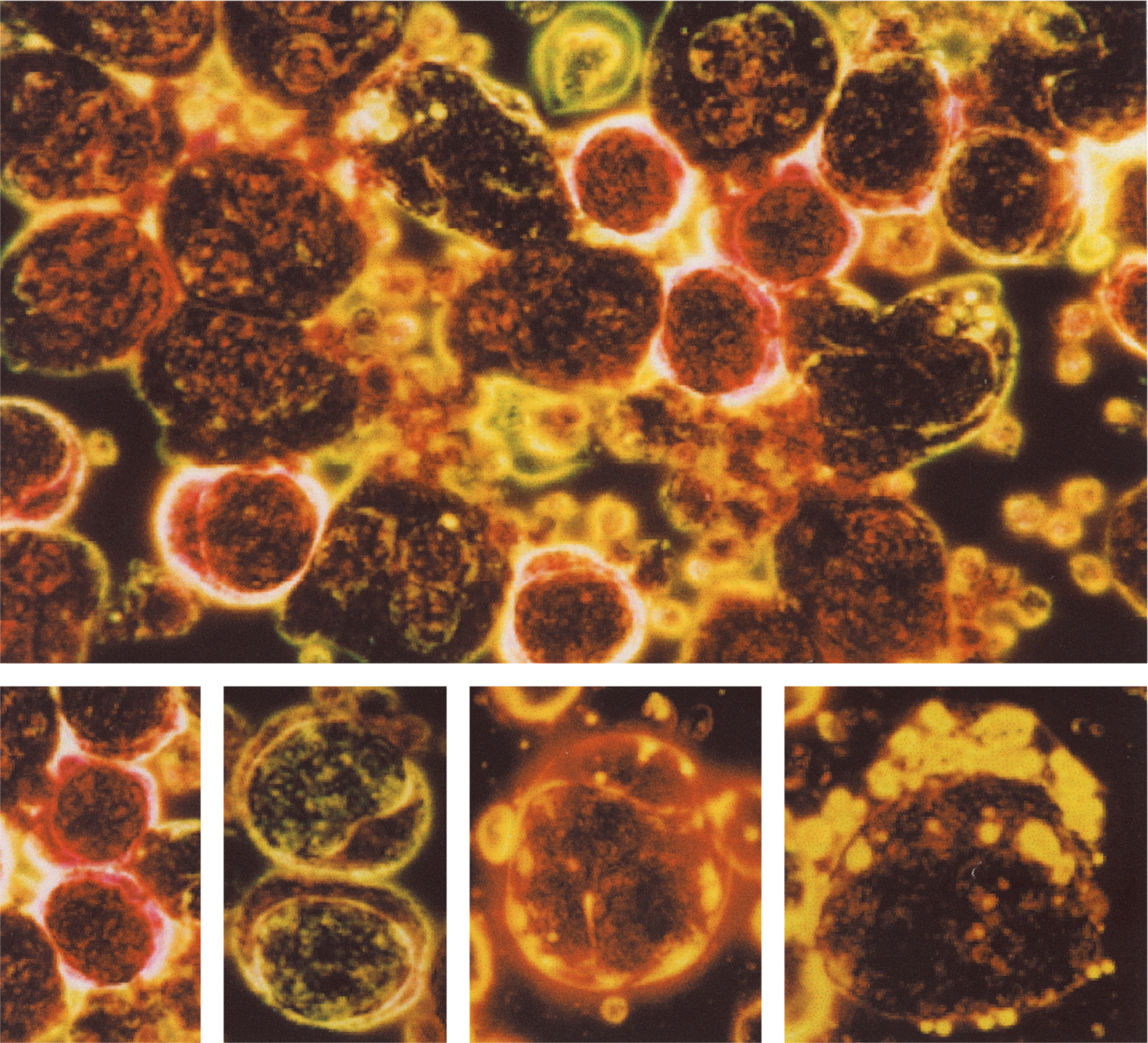
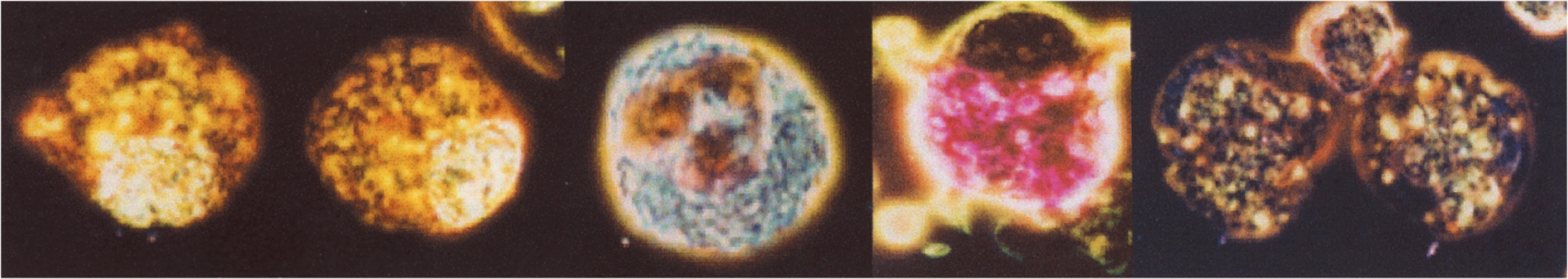
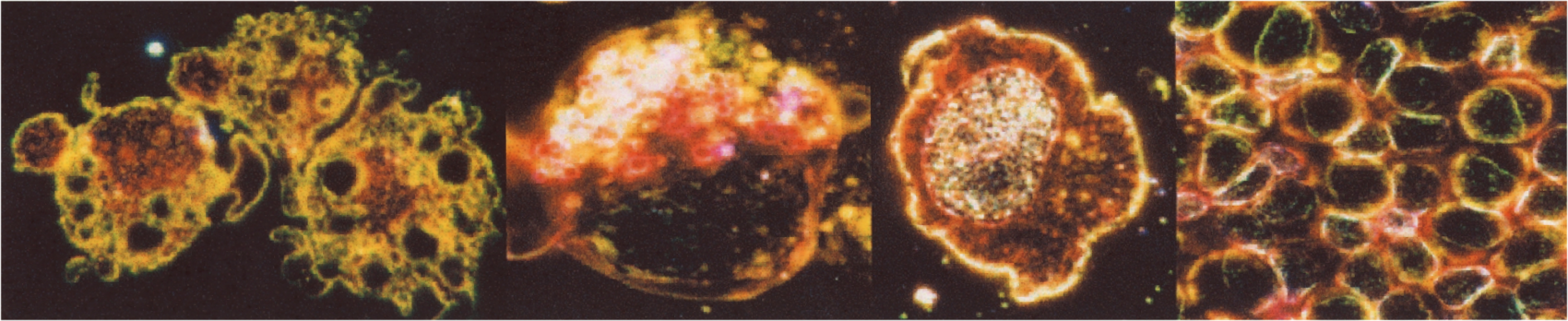
When stained with LYMPHOCOLOR and viewed under darkfield illumination, cells from peripheral blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes display a variety of colors against a black background. Particularly, B lymphocytes stain bright yellow, T helper cells (CD4) stain bright red, T cytotoxic/suppressor cells (CD8) stain bright yellow orange, and natural killer (NK) cells stain green and contain green granules. When it is employed in conjunction with monoclonal antibody techniques for identification of lymphocyte subpopulations, staining of lymphocytes with LYMPHOCOLOR can serve as a rapid screening technique, and help to identify which specimens require further analysis by other methodologies, including flow cytometry.
Principle :
LYMPHOCOLOR is a substantially pure dye that imparts brilliant and differential coloration of lymphocytes revealed under dark field illumination.
Reagents :
1. FAA Fixative.
2. LYMPHOCOLOR stain.
3. Buffer.
Materials :
1. Microscope equipped with dark field oil condenser and oil immersion lens equipped with an iris diaphragm.
Procedure :
1. Fix cover slips containing peripheral blood, buffy coat, lumph node imprint, or bone marrow aspirate in FAA fixative for 5 minutes.
2. Wash in running distilled water for 1 minute.
3. Stain with LYMPHOCOLOR for 10 minutes. The presence of undissolved dye particles in the stain solution does not affect the performance of the stain.
4. With a forceps, grasp cover slip containing stained cells, and drain off the stain onto filter paper. Dip cover slip into a small beaker containing the buffer, and agitate vigorously for exactly 2 seconds.
5. Blot dry with filter paper, and mount with xylene based synthetic resin mounting medium on cleaned glass slides, and view under dark field illumination.
Results :
Granules in neutrophils stain dark red black. In eosinophils, granules stain bright blue. In basophils, granules stain bright pink. In monocytes, nuclei and cytoplasm stain bright green, and nuclei show typical convolutions and indentations. In some monocytes, yellow stained vacuoles are visualized. In cell sorter studies using monoclonal antibodies to obtain individual lymphocyte subpopulations of high purity, LYMPHOCOLOR stains B cells yellow, T helper cells bright red, T cytotoxic/supressor cells yellow orange, and natural killer (NK) cells bright green with green granules. In some B cells, multiple yellow annular appearing structures occur in the cytoplasm.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT FOR USE IN HUMAN DIAGNOSTICS
Lymphocolor Kit Includes:
1 - 2 oz. Stain
1 - 2 oz. FAA Fixative
2 - 4 oz. Buffer
$60.00 per kit
~ sufficient for 120 slides or 240 coverslips