A fast stain for hematology and cytology.
Intended Use :
RAPIDIFF is a quick, general purpose stain for blood and bone marrow cells. With a few exceptions, it stains these cells similarly to a traditional stain, like Wright's or Giemsa's. RAPIDIFF is superior to these stains because the staining time is faster and the details of nuclei and cytoplasm are more precisely and intensely colored. RAPIDIFF can also be used to stain imprints, cytological smears, cytospins, and fine needle aspirates (FNA's).
Principle :
Coverslips or slides containing unfixed blood or bone marrow cells are exposed first to a methanolic solution of a basic azo dye, then to a mixture of methanol and an aqueous alkaline buffered solution of the same azo dye.Colors in cells are developed fully by a brief rinse in a mildly acidic phosphate buffer.
Reagents :
1. Solution A, a methanolic solution of a basic azo dye.
2. Solution B, an aqueous alkaline buffered solution of the same dye, to which a small amount ofmethanol has been added. Both solutions A and B can be kept at room temperature in covered Coplin jars. The presence of undissolved particles does not affect the performance of the stain.
3. pH 6.8 Phosphate Buffer. Add all of the buffer salt crystals to a 1 L volumetric flask add distilled water to make 1 L. Dissolve any remaining crystals in the tube with a small amount of distilled water, and add to the 1 L flask. To retard bacterial growth, add 10 drops phenol to the buffer, place in a stoppered glass bottle or a plastic container, and store at 5 degrees C in the refrigerator. Prepared and stored in this way, the buffer is stable for 1 year. Do not use the buffer if the solution shows obvious contamination.
Procedure :
1. Make smear preparations of peripheral blood, bone marrow, or buffy coat and air dry Cytocentrifuge preparations, imprints, cytological smears or fine needle aspirates (FNA) can be used.
DO NOT FIX ANY OF THE SLIDES.
DO NOT HEAT FIX SLIDES.
2. Place blood smear slide in a Coplin jar containing solution A for 15 seconds. Grasp slide, and place it in the Coplin jar containing solution B for 15 seconds. For veterinary blood smears, place slide in solution A for 15 seconds and in solution B for 90 seconds.
3. For bone marrow, cytospins, imprints, cytological smears, swabs, and fine needle aspirates, leave in solution A for 30 seconds, and then in solution B for 15-30 seconds.The longer the slide is left in solution B, the darker the stain will be.
4. Grasp slides or cover slips with forceps, and agitate VERY VIGOROUSLY to and fro for 10 seconds in 6.8 pH buffer contained in a small beaker.
5. Wash again in the same way for 10 seconds in second beaker containing fresh buffer. Both beakers containing buffer can be covered and used for 30 slides or 60 cover slips.
6. Drain dry rather than blot dry. For optimal color perception, remove any blue filter covering the light source of the microscope, and replace it with a didymium filter.
Results :
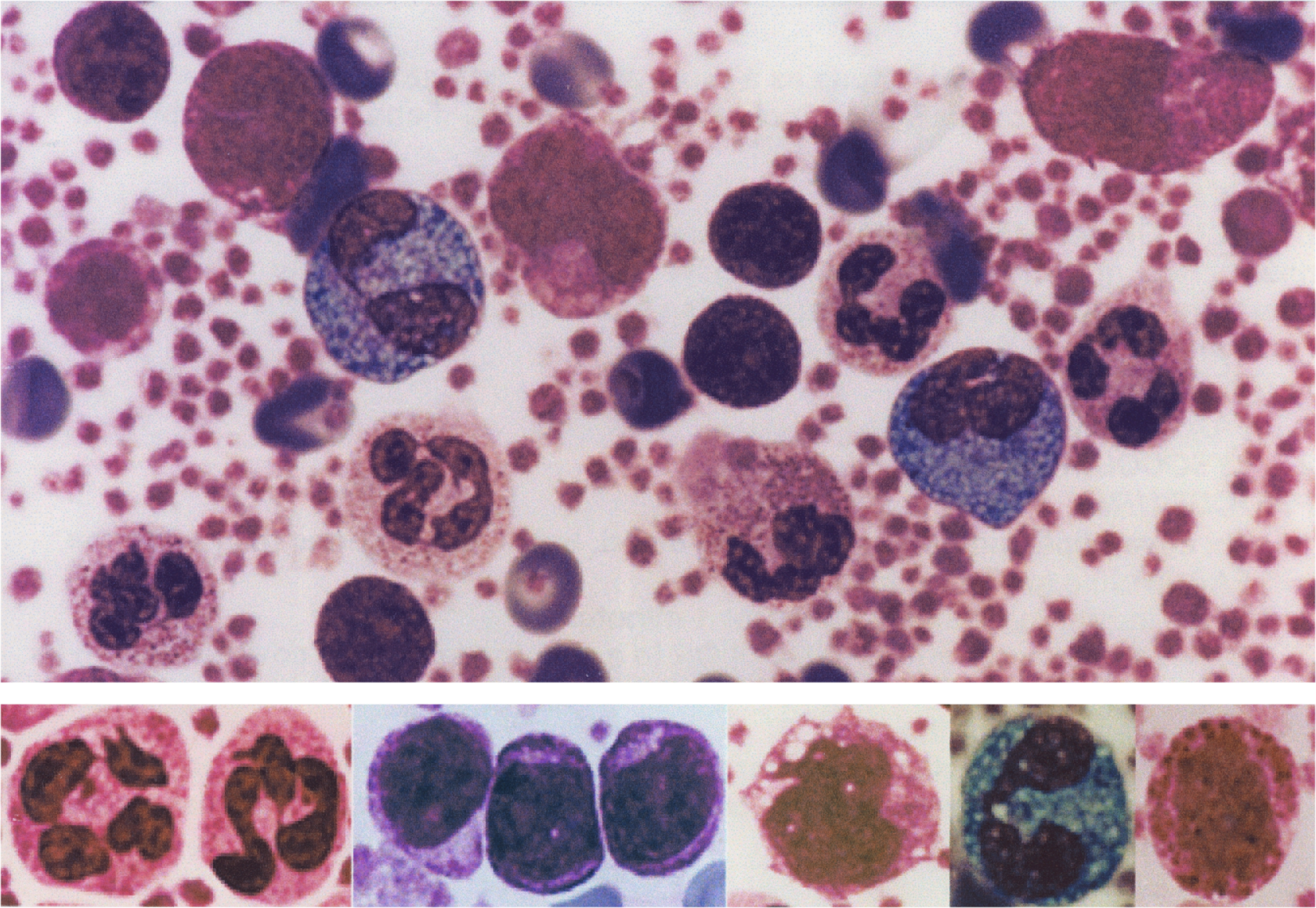
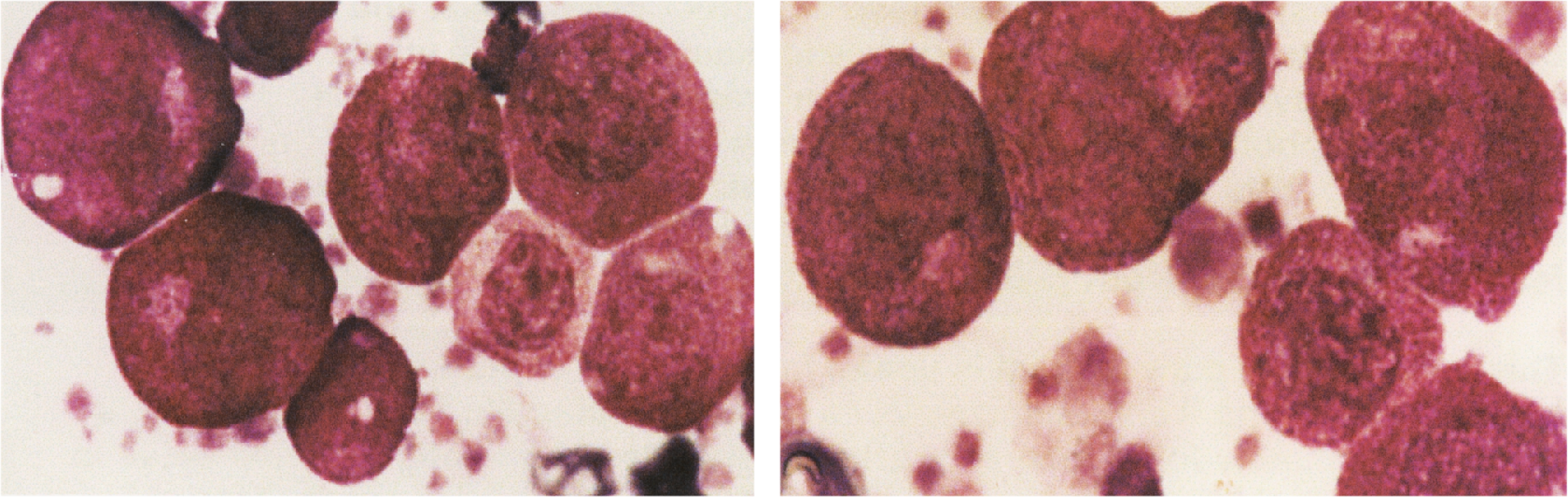
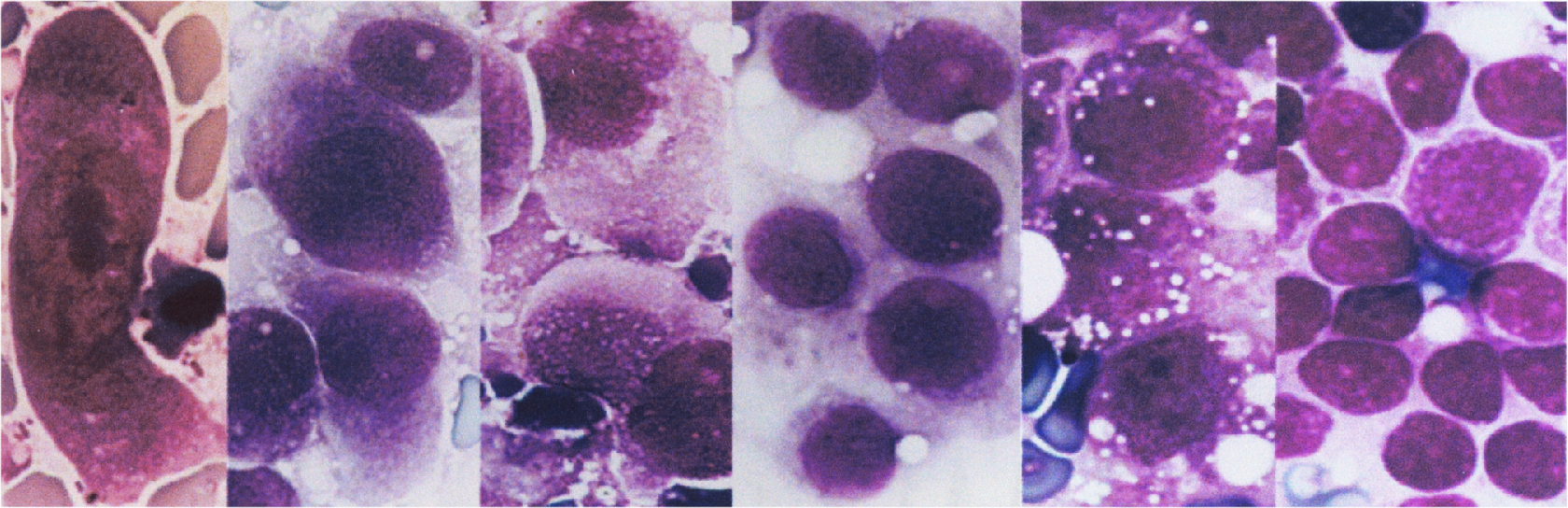
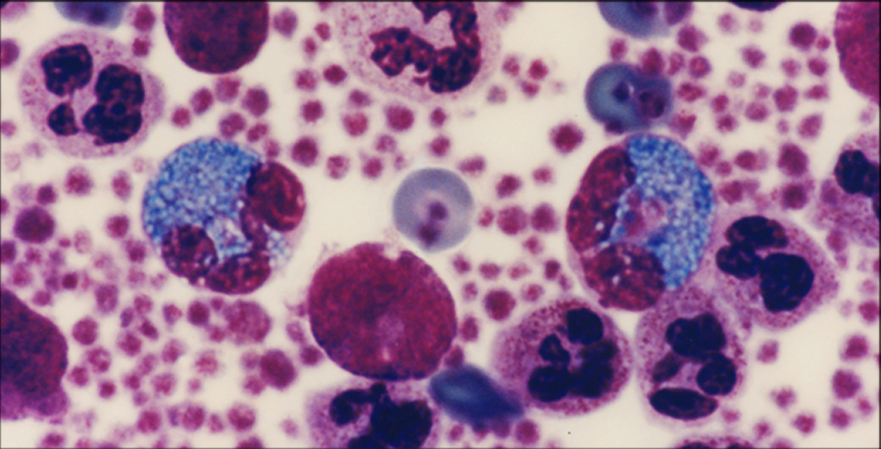
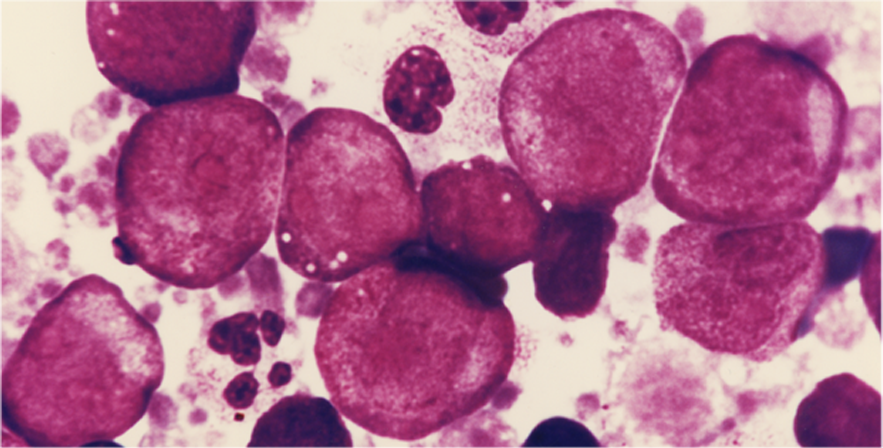
Except for eosinophil granules that stain turquoise blue and erythrocytes that stain orange green, all of the other colors in blood and bone marrow cells are the same as those found with traditional stains. However, colors are more intense and cellular details are more precise than obtained with traditional stains. Granules in basophils and mast cells stain bright red purple. Erythrocytic inclusions such as malarial parasites stain vividly, and polychromatophilic erythrocytes are distinguished easily from other erythrocytes. Nucleoli and nuclear chromatin strands stain intensely and precisely.
Rapidiff Kit Includes:
1 - 4 oz. Solution A
1 - 4 oz. Solution B
1 - Tube Buffer Salts
$60.00 per kit
~ sufficient for 250 slides or 500 coverslips